Difference between revisions of "Looseness"
(Created page with "<p align=center> 300px </p> ==Loosenes - Loose grain leather== '''"Losnarbig"''' ist Leder, wenn seine Narbenschicht von ...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Looseness - Loose grain leather== |
| − | + | Normally, leather fibres are very closely knit, making it virtually impossible to see any gaps or weaknesses. But, if the grain layer of the leather is of irregular thickness and density, it is described as looseness of leather or loose grain leather. In some cases the looseness is so pronounced that the surface can be separated from the lower leather layers by using your finger and such leather tends to get a very wrinkly appearance when folded. | |
| − | + | The cause is mainly due to fat deposits in the animal [[Hide - Skin|skin]], which dissolve during [[leather production|tanning]] and leave cavities. The hides of [[Sheep leather|sheep]] and [[Lamb leather|lamb]] are particularly susceptible to looseness. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 16: | Line 14: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''In loose-grain leathers, the fibre braid is loose under the grain layer. Cow leather pulled apart with fingernail.''</p> |
| − | + | This can also affect [[cow leather]]. Normally, such hides are sorted out in [[leather production|production]]. Loose grain in bovine leather is down to nutrition (fatty fodder) or an interruption in the [[Preservation by drying, salting or freezing|cooling process]] of the untanned skin. The fat in the skin then spoils and weakens the fibres. Certain breeds of cattle are more prone to this phenomenon. For e.g. cross-breeds are more susceptible. | |
| − | + | The main problem with bovine leather is the "loose-grained effect". This occurs when the applied [[finish|colour layer (pigmentation)]] is firmer than the leather underneath. The colour layer floats on the soft leather layer causing unwanted wrinkles to appear. | |
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-01.jpg| | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-01.jpg|500px]] |
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-02.jpg| | + | </p> |
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-02.jpg|500px]] | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-03.jpg| | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-03.jpg|500px]] |
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-04.jpg| | + | </p> |
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-04.jpg|500px]] | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Typical cases of looseness.''</p> |
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-06.jpg| | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-06.jpg|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-07.jpg|500px]] |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''Looseness is not necessarily distributed throughout the complete skin.''</p> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 57: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Both cross-sections are from the same skin. The different fibre structures are easy to recognise. The loose grain is in the region of the thicker fibre bundles.''</p> |
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-14.jpg| | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-14.jpg|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit- | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-12.jpg|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | |||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-11.jpg|500px]] | |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Losnarbigkeit-15.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''This [[car leather|car head support]] shows very different wrinkles within a small area. The leather is looser in the margins. With a headrest, this is not necessarily a [[leather quality|quality deficiency]].''<br></p> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional information == | == Additional information == | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Leather damages]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Natural markings on leather]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Leather defects]] |
| − | < | + | <logoplustext /> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Kategorie:All Articles]] | [[Kategorie:All Articles]] | ||
[[Kategorie:Leather types]] | [[Kategorie:Leather types]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:03, 28 September 2022
Looseness - Loose grain leather
Normally, leather fibres are very closely knit, making it virtually impossible to see any gaps or weaknesses. But, if the grain layer of the leather is of irregular thickness and density, it is described as looseness of leather or loose grain leather. In some cases the looseness is so pronounced that the surface can be separated from the lower leather layers by using your finger and such leather tends to get a very wrinkly appearance when folded.
The cause is mainly due to fat deposits in the animal skin, which dissolve during tanning and leave cavities. The hides of sheep and lamb are particularly susceptible to looseness.
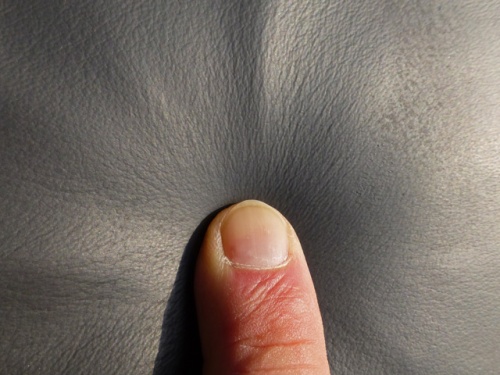
In loose-grain leathers, the fibre braid is loose under the grain layer. Cow leather pulled apart with fingernail.
This can also affect cow leather. Normally, such hides are sorted out in production. Loose grain in bovine leather is down to nutrition (fatty fodder) or an interruption in the cooling process of the untanned skin. The fat in the skin then spoils and weakens the fibres. Certain breeds of cattle are more prone to this phenomenon. For e.g. cross-breeds are more susceptible.
The main problem with bovine leather is the "loose-grained effect". This occurs when the applied colour layer (pigmentation) is firmer than the leather underneath. The colour layer floats on the soft leather layer causing unwanted wrinkles to appear.
Typical cases of looseness.
Looseness is not necessarily distributed throughout the complete skin.
Both cross-sections are from the same skin. The different fibre structures are easy to recognise. The loose grain is in the region of the thicker fibre bundles.
This car head support shows very different wrinkles within a small area. The leather is looser in the margins. With a headrest, this is not necessarily a quality deficiency.
Additional information




















 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution