Difference between revisions of "Leather damages"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| − | There are various types of leather | + | There are various types of leather damage. It can tear, suffer burn holes, [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|fade in sunlight]] or become brittle. Leather can also become hard due to ageing. |
==Signs of wear on leather== | ==Signs of wear on leather== | ||
| − | Leather is a [[leather quality|durable material]]. | + | Leather is a [[leather quality|durable material]]. That is why it was used long ago as [[Leather saddle|material for saddles]] or [[leather tents & Tent walls|tarpaulins]]. Nowadays, [[car leather|car seats]] or [[leather furniture|furniture]] covers made of leather are considered to be durable and of high [[leather quality|quality]]. Leather is often mechanically stressed, leading to general signs of wear and traces of use. The surface is scratched or the [[finish|surface colour]] rubs off. |
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | As long as the damages are not too | + | As long as the damages are not too severe, most of them can be coloured, filled and [[Leather repair|repaired]] by suitable [[leather care]] and can be protected against further wear. |
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
Sweat and body grease from skin or the oils from the hair penetrate the surface of the leather. This is caused over a period of time and due to regular contact. These fats oxidize (degrade) and deprive the leather of the effect of the [[tannins]]. The leather fibre loses its structure and disintegrates. The [[pH value|pH value]] of the sweat can also be a contributing factor. | Sweat and body grease from skin or the oils from the hair penetrate the surface of the leather. This is caused over a period of time and due to regular contact. These fats oxidize (degrade) and deprive the leather of the effect of the [[tannins]]. The leather fibre loses its structure and disintegrates. The [[pH value|pH value]] of the sweat can also be a contributing factor. | ||
| − | Typical areas for such damages are [[car leather|armrests of cars]], [[Leather steering wheel|steering wheels]] and [[leather furniture|furniture]]. Men sweat more. Therefore, the disintegration is always particularly strong | + | Typical areas for such damages are [[car leather|armrests of cars]], [[Leather steering wheel|steering wheels]] and [[leather furniture|furniture]]. Men sweat more. Therefore, the disintegration is always particularly strong where men have contact with leather. Regular [[leather cleaner|cleaning]] and [[leather care|maintaining]] of the leather delays such changes significantly. Furniture should also be provided with blankets or pillows in permanent skin and hair contact areas. Oxidative damage from skin and hair are caused by continuous use. With regular cleaning and care treatments, the process can be significantly delayed. |
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''Typical fat damages: | + | ''Typical fat damages: Grease on the collar in [[leather clothing|clothing]] or sweat damages in [[leather shoes|shoes]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | + | The question frequently arises in the [[leather furniture|furniture sector]] whether the consumption of medication and the subsequent perspiration contributes to leather damage and ageing. Since there is hardly a person who has not taken medication at some time, their leather clothing, including shoes, does not appear to have suffered perceptibly. Therefore the basic risk from medication must be discounted. Only in a very few individual cases, which may be associated with liver disease, there does appear to be medicines that change the sweat in such a way that the leather ages more rapidly and becomes fragile, even during the warranty period. However, this has not been subject to scientific investigation and such cases are rare. | |
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''The professional cleaning and [[Leather repair|colouration]] | + | ''The professional cleaning and [[Leather repair|colouration]] of slightly damaged [[leather furniture|furniture leather]].''<br></p> |
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
== [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|Fading of leather]]== | == [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|Fading of leather]]== | ||
| − | Some leathers are fade-sensitive and | + | Some leathers are fade-sensitive and contain no high [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|light protection factor]]. In particular, [[suede]], [[nubuck]] and [[aniline leather]] are fade-sensitive. This phenomenon is rare in [[finish|strongly pigmented]] leather, since most pigments are insensitive for fading. [[leather colour|Aniline dyes]] are much more sensitive and tend to fade stronger and faster. [[car leather|Automobile leathers]] are generally [[finish|highly pigmented]] and rarely fade. |
| − | Such leathers should therefore be treated with [[leather care|care products]] with UV protection. | + | Such leathers should therefore be treated with [[leather care|care products]] with UV protection. Although these cannot prevent fading, they can delay it. |
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''Fading can happen on velvet like surfaces like [[suede]] and [[nubuck]], but also on [[finish|pigmented leather]].''<br></p> | + | ''Fading can happen on velvet-like surfaces like [[suede]] and [[nubuck]], but also on [[finish|pigmented leather]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''Faded [[car leather]]. Behind panels or the | + | ''Faded [[car leather]]. Behind panels or the original belt.''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | + | Leather usually becomes brighter with exposure to light. The exception is [[Vegetable-tanned leather|vegetable-tanned]], uncoloured leather, which darkens with time. As this is a desired effect it is not considered to be damaging. The leather should then be exposed to light in such a way that the leather darkens evenly. | |
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
==Disintegration of old leather== | ==Disintegration of old leather== | ||
| − | + | While the [[tanner]] tries to produce the best [[leather quality|quality leather]], it still decays with time, even with careful use and optimal storage. [[Antique Leather - Vintage Leather|Very old leather]] begins to become fibrous and decompose, while other leather can also harden and stiffen. | |
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''[[Antique Leather - Vintage Leather| | + | ''Hardening or decay of [[Antique Leather - Vintage Leather|antique Leather]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 12 April 2017
There are various types of leather damage. It can tear, suffer burn holes, fade in sunlight or become brittle. Leather can also become hard due to ageing.
Contents
Signs of wear on leather
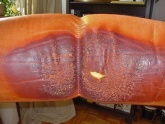
Leather is a durable material. That is why it was used long ago as material for saddles or tarpaulins. Nowadays, car seats or furniture covers made of leather are considered to be durable and of high quality. Leather is often mechanically stressed, leading to general signs of wear and traces of use. The surface is scratched or the surface colour rubs off.
Typical wear on car and furniture leather.
As long as the damages are not too severe, most of them can be coloured, filled and repaired by suitable leather care and can be protected against further wear.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF CAR LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF CAR LEATHER
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF FURNITURE LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF FURNITURE LEATHER
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Leather quality
Traces of use and signs of wear can look different and depend largely on the quality of the leather and the colour.
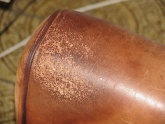
When the leather is of good substance, the finish (surface pigmentation) rubs off over time. The leather itself remains undamaged. If the leather itself is unstable, the leather cracks under the finish and the paint layer cannot withstand the lack of stability in the fibre structure of the leather.
Typical wear on good quality car and furniture leather.
Typical cracks in leather with poorer leather quality.
- Further information: Leather quality
Grease and sweat stains on leather
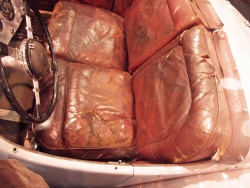
Sweat and body grease from skin or the oils from the hair penetrate the surface of the leather. This is caused over a period of time and due to regular contact. These fats oxidize (degrade) and deprive the leather of the effect of the tannins. The leather fibre loses its structure and disintegrates. The pH value of the sweat can also be a contributing factor.
Typical areas for such damages are armrests of cars, steering wheels and furniture. Men sweat more. Therefore, the disintegration is always particularly strong where men have contact with leather. Regular cleaning and maintaining of the leather delays such changes significantly. Furniture should also be provided with blankets or pillows in permanent skin and hair contact areas. Oxidative damage from skin and hair are caused by continuous use. With regular cleaning and care treatments, the process can be significantly delayed.
Typical changes of car arm rests after continuous use.
Typical damage of steering wheels.
Typical fat damages: Grease on the collar in clothing or sweat damages in shoes.
Typical changes of furniture in head and armrest areas.
The question frequently arises in the furniture sector whether the consumption of medication and the subsequent perspiration contributes to leather damage and ageing. Since there is hardly a person who has not taken medication at some time, their leather clothing, including shoes, does not appear to have suffered perceptibly. Therefore the basic risk from medication must be discounted. Only in a very few individual cases, which may be associated with liver disease, there does appear to be medicines that change the sweat in such a way that the leather ages more rapidly and becomes fragile, even during the warranty period. However, this has not been subject to scientific investigation and such cases are rare.
The professional cleaning and colouration of slightly damaged furniture leather.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - GREASY STAINS ON HEAD OR ARMREST AREAS
-> COLOURLOCK - GREASY STAINS ON HEAD OR ARMREST AREAS
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Fading of leather
Some leathers are fade-sensitive and contain no high light protection factor. In particular, suede, nubuck and aniline leather are fade-sensitive. This phenomenon is rare in strongly pigmented leather, since most pigments are insensitive for fading. Aniline dyes are much more sensitive and tend to fade stronger and faster. Automobile leathers are generally highly pigmented and rarely fade.
Such leathers should therefore be treated with care products with UV protection. Although these cannot prevent fading, they can delay it.
Fading can happen on velvet-like surfaces like suede and nubuck, but also on pigmented leather.
Faded leather furniture.
Faded car leather. Behind panels or the original belt.
The most common phenomenon of colour change in leather is fading. But there are also rare cases of yellowing.
Yellowing of car leather. A rare phenomenon.
Leather usually becomes brighter with exposure to light. The exception is vegetable-tanned, uncoloured leather, which darkens with time. As this is a desired effect it is not considered to be damaging. The leather should then be exposed to light in such a way that the leather darkens evenly.
Darkened, vegetable-tanned smooth leather.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - CLEANING AND CARE OF ANILINE LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - CLEANING AND CARE OF ANILINE LEATHER
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - CLEANING AND CARE OF NUBUCK AND SUEDE
-> COLOURLOCK - CLEANING AND CARE OF NUBUCK AND SUEDE
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Disintegration of old leather
While the tanner tries to produce the best quality leather, it still decays with time, even with careful use and optimal storage. Very old leather begins to become fibrous and decompose, while other leather can also harden and stiffen.
Hardening or decay of antique Leather.
The patination of an antique leather folder.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - THE TREATMENT OF ANTIQUE LEATHER / CHESTERFIELD LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - THE TREATMENT OF ANTIQUE LEATHER / CHESTERFIELD LEATHER
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - THE TREATMENT OF HARDENED LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - THE TREATMENT OF HARDENED LEATHER
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Dye transfer on leather
In the past, the cases where clothing or fabrics discolour leather or imitation leather have increased. This always applies to lighter colours because the discolourations are better visible on light surfaces. These are usually furniture or car leathers. Jackets, trousers or leather belts mainly cause these discolourations. Some cushions can leave dye stains on furniture or socks can lead to dye transfer on shoes. The processed jeans, textile or leather transfer dyes to the leather surfaces of the upholstery. The dyes slowly sink into the leather or artificial leather surface. These stains cannot be removed by means of standard cleaners.
Typical denim discolouration on car leather.
Belt discolourations on car leather are usually so strong that only a specialist company can help.
The sensitivity to such discolouration has increased significantly over the past 15 years. In most cases the dying materials are blamed. But leather that is older than 15 years tends to be significantly less stained, even when they come into contact with the colouring materials. Therefore, it can be assumed that the change from solvent products to water-based finish-chemicals of leather and synthetic leather and the trend towards very matt surfaces have markedly increased this sensitivity. It is therefore common to find more adverts from chemical companies who have developed new additives with "anti-soiling properties".
Colouration by protective covers made of sheepskin. Left leather, right synthetic leather.
Unfortunately, brand new, light upholstery furniture after a short time dirts by discolouration of textiles (not only jeans!) And there is no easy cleaning possibility.
A simple test is sufficient: Lightly moisten a light cloth and make a rubbing test on the discolouring material. Does it dye strong, the discolouration is too much. There are also cases where leggings, which do not rub off during the rubbing test, still discolour the upholstery. It is therefore necessary to examine from case to case the fault of the discolouration. In case of doubt, an expert or institute has to check.
Too strong dye transfer from leather shoes and leather jackets.
Typical jeans discolouration.
Discolouration by the back of a fur blanket on furniture.
Strong discolouring leggings stain new artificial leather sofa.
A typical case: Pillows discolour new artificial leather.
Jeans discolouration on handbag leather. - Patent leather is extremely sensitive and discolours easily.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - HOW TO REMOVE TEXTILE DISCOLOURATION
-> COLOURLOCK - HOW TO REMOVE TEXTILE DISCOLOURATION
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Other leather damages
- Typical split leather damages
- Typical damage to PU leather in the furniture area
- Colour separation of leather
- Damage to synthetic leather with leather fibres on the reverse
- Flamingo effect: Reddish discolourations on bright furniture in concealed areas
- Bronzing: Metallic glimmer on new leather
- Glue migration from the back side to the visible side of the leather
- Stains on perforations
- Colour migration from behind the leather through to the front
- Dye transfer from leather
- Tyre marks on car leather
- Mouldy leather
- Fatty spue - Fat marks on leather
- Corrosion on contact of metals and leather
- Salt stains on shoes and boots
- Shrunken leather - leather shrinkage
- Dents - Over stretching - Sagging in leather
- Looseness
- Cat scratches on leather
- Vermin damage on leather
- Red decay
- Cowhides and bald spots
- False pH value
- Too slippery Leather
- Spinn web effect caused by aziridine crosslinkers
- Electrostatic charging of leather
Additional information
- Leather repair
- Basic rules when dealing with leather
- Natural markings on leather (Scars, skin diseases, brand marks etc.)
- Leather defects
- Leather defects (Errors in the leather production)


































































 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution