Leather damages
There are various different types of leather damages. Leather damage can happen through accidents. Leather can tear, can get burn holes, leather can fade by sund light or become brittle. Leather can become hard due to aging.
Contents
Signs of wear on leather
Leather is a durable material. Therefore, it was used long ago as material for saddles or tarpaulins. Nowadays, car or furniture covers made of leather are considered to be durable and of high quality. Leather is often mechanically stressed and there are traces of use. The surface is scratched or the surface colour rubs off.
Typical wear on car and furniture leather.
As long as the damages are not too strong, most of them can be beautified and repaired by suitable leather care and can be protected against further wear.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF CAR LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF CAR LEATHER
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF FURNITURE LEATHER
-> COLOURLOCK - TREATMENT OF FURNITURE LEATHER
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Leather quality
Depending on the quality of the leather and the colour, the look of the traces of use are different.
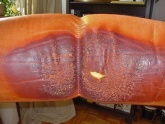
When the leather is of good substance, the finish (surface pigmentation) rubs off over time. The leather itself remains undamaged. If the leather itself is unstable, the leather cracks under the finish and the paint layer can not absorb the lack of stability in the fiber struchture of the leather.
Typical wear of good quality car and furniture leather.
Typical cracks in leather with poorer leather quality.
- Further information: Leather quality
Grease and sweat stains on leather
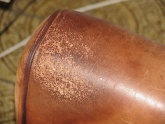
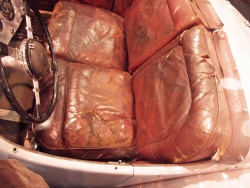
Sweat of the skin or the fats in the hair migrate through regular contact into the leather. These fats oxidize (degrade) and deprive the leather of the effect of the tannins, which consume in the fight against the oxidation of the external applied fats. The leather fibre loses its structure and disintegrates. The pH value of the sweat also contributes.
Typical for such areas are armrests of cars, steering wheels and furniture. Men sweat more. Therefore the disintegration is always particularly strong, where men have contacts with leather. A regular cleaning and maintaining of the leather delays such changes significantly. Furniture should also be provided with blankets or pillows in permanent skin and hear contact areas. Oxidative damage caused by skin and hair are caused by continuous use. In case of regualr cleaning and care treatments, the process can be significantly delayed.
Typical changes of car arm rests after continuous use.
Typical damage of [[[Leather steering wheel|steering wheels]].
Typical fat damages: Fat collar in clothing or sweat damages in shoes.
Typical changes of furniture in head and armrest areas.
Particularly in the furniture sector, the question frequently arises whether the consumption of medication and the subsequent perspiration promotes the aging of leather or the development of leather damage. Since there is hardly a person who can manage completely without medication and his leather clothing including shoes do not suffer perceptibly, a basic risk of medication must be denied. Only in very few individual cases, which may be associated with liver diseases, there appears to be medicines that change the sweat in such a way that the leather ages more rapidly and becomes fragile even during the warranty period. However, a scientific investigation has not yet taken place and the cases are rare.
The professional cleaning and colouration on not too damaged furniture leather.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - GREASY STAINS ON HEAD OR ARMREST AREAS
-> COLOURLOCK - GREASY STAINS ON HEAD OR ARMREST AREAS
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Fading of leather
Manche Leder sind ausbleichempfindlich und haben keinen hohen Lichtschutzfaktor. Insbesondere Rauleder und Anilinleder sind ausbleichempfindlich. Bei stark pigmentierten Ledern ist dieses Phänomen eher selten, da die meisten Pigmente gut gegen Ausbleichen eingestellt sind. Die Anilinfarben sind dagegen deutlich empfindlicher und neigen viel stärker zum Ausbleichen. Autoleder sind in der Regel stark pigmentiert und bleichen nur in ganz seltenen Fällen aus.
Solche Leder sollten daher mit Pflegemitteln mit UV-Schutz behandelt werden. Dieses können das Ausbleichen nicht verhindern, aber deutlich verzögern.
Ausbleichungen können Rau- und Glattleder betreffen.
Ausgeblichene Nubuk- und Velourleder
Ausgeblichenes Möbelleder.
Ausgeblichenes Auto-. Hinter der Verkleidung oder dem Gurt noch original.
Das häufigste Phänomen der Farbveränderung bei Ledern ist das Ausbleichen. Aber es gibt auch seltene Fälle von Vergilbungen.
Eine Vergilbung bei Autoleder - ein seltenes Phänomen
Bis auf pflanzlich gegerbte, ungefärbte Leder, werden Leder durch den Lichteinfluss heller. Nur pflanzlich gegerbte Naturleder dunkeln mit der Zeit nach. Dieser Effekt ist auch ein gewünschte Effekt und kein Lederschaden. Das Leder sollte dann aber so gelagert werden, dass der Lichteinfall das Leder gleichmäßig dunkelt.
Nachgedunkeltes, pflanzlich gegerbtes, ungefärbtes Glattleder
- Lichtechtheit
- Hilfe bei verblichenen Anilinledern bei Möbeln
- Hilfe bei verblichenen Rauledern bei Möbeln
Disintegration of old leather
So sehr sich der Gerber auch Mühe gibt, aber irgendwann zerfällt auch Leder, selbst bei schonender Nutzung und optimalen Lagerung. Bei Antikledern fängt das Leder irgendwann an faserig zu werden und zu zerfallen oder manche Leder verhärten auch und werden unbeweglich.
Antike Leder zerfallen oder verhärten (Sattel)
Die Nachpatinierung einer antiken Mappe.
- Die Restauration antiker Stühle
- Die Behandlung sehr alter Autoleder
- Die Restauration alter Arztkoffer
- Die Behandlung antiker Pistolentaschen
Dye transfer on leather
In the past, the cases where clothing or fabrics discolour leather or imitation leather have increased. This always applies to lighter colours because the discolourations are better visible on light surfaces. These are usually furniture or car leathers. Jackets, trousers or leather belts are causing the discolourations. Sometimes also cushions or even socks are the causing objects. The processed jeans, textile or leather transfere dyes to the leather surfaces of the upholstery. The dyes slowly sink into the leather or artificial leather surface. These stains can not be removed by means of standard cleaners.
Typical denim discolouration on car leather.
Belt discolorations on car leather are usually so strong that only a specialist company can help.
The sensitivity to such discolouration has increased significantly over the past 15 years. In most cases the dying materials are blamed. But leather that is older than 15 years tends to be significantly less stained, even when they come into contact with the coloring materials. Therefore it can be assumed that the change from solvent products to water-based finish-chemicals of leather and synthetic leather and the trend towards very matt surfaces have markedly increased this sensitivity. In the advertising of the chemical industry, therefore more and more additives with "anti-soiling properties" appear.
Colouration by protective covers made of sheepskin. Left leather, right synthetic leather.
Unfortunately, brand new, light upholstery furniture after a short time dirts by discoloration of textiles (not only jeans!) And there is no easy cleaning possibility.
A simple test is sufficient: Lightly moisten a light cloth and make a rubbing test on the discolouring material. Does it dye strong, the discolouration is too much. There are also cases where leggings, which do not rub off during the rubbing test, still discolor the upholstery. It is therefore necessary to examine from case to case the fault of the discoloration. In case of doubt, an expert or institute has to check.
Too strong dye transfer from leather shoes and leather jackets.
Typical jeans discoloration.
Discoloration by the back of a fur blanket on furniture.
Strong discolouring leggings stain new artificial leather sofa.
A typical case: Pillows discolour new artificial leather.
Jeans discoloration on handbag leather. - Patent leather is extremely sensitive and discolors easily.
![]() -> COLOURLOCK - HOW TO REMOVE TEXTILE DISCOLOURATION
-> COLOURLOCK - HOW TO REMOVE TEXTILE DISCOLOURATION
![]() -> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
-> In German: www.lederzentrum.de
![]() -> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
-> Rest of the world: partners worldwide
Other leather damages
- Typical split leather damages
- Typical damage to PU leather in the furniture area
- Colour separation of leather
- Damage to synthetic leather with leather fibres on the reverse
- Flamingo effect: Reddish discolourations on bright furniture in concealed areas
- Bronzing: Metallic glimmer on new leather
- Glue penetration from the back side to the visible side of the leather
- Stains on perforations
- Colour migration from behind the leather through to the front
- Dye transfer from leather
- Tire marks on car leather
- Mouldy leather
- Fatty spue - Fat marks on leather
- Corrosion on contact of metals and leather
- Salt stains on shoes and boots
- Shrunken leather - leather shrinkage
- Dents - Over stretching - Sagging in leather
- Looseness
- Cat scratches on leather
- Vermin damage on leather
- Red rot
- Cowhides and bald spots
- False pH value
- Too slippery Leather
- Spinn web effect caused by aziridine crosslinkers
- Electrostatic charging of leather
Additional information
- Leather repair
- Basic rules when dealing with leather
- Natural markings on leather (Scars, skin diseases, brand marks etc.)
- Leather defects
- Leather defects (Errors in the leather production)
































































 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution