Difference between revisions of "Leather quality"
m |
m |
||
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
To test the various requirements for leather, there are a wide variety of test devices. | To test the various requirements for leather, there are a wide variety of test devices. | ||
| − | * '''VESLIC rubbing test''': The rubbing test checks the dry abrasion and wet abrasion. Wool felts are rubbed dry and wet in a specified number of times over the leather. The wear in daily use and the prone to discolouration is examined. | + | * '''VESLIC rubbing test''': The rubbing test checks the dry abrasion and wet abrasion qualities of leather. Wool felts are rubbed dry and wet in a specified number of times over the leather. The wear in daily use and the prone to discolouration is examined. |
| Line 183: | Line 183: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | * '''[[Leather flexometer test]]''': This test examines | + | * '''[[Leather flexometer test]]''': This test examines resistance of the leather to wrinkles. Folding the leather multiple times in all directions allows it to test its resitance. |
| − | In particular, [[Leather shoes|shoe upper leather]] gets buckled during walking and needs a special resistance to [[Leather damages|breakage]]. | + | In particular, [[Leather shoes|shoe upper leather]] gets buckled during walking and needs a special resistance to [[Leather damages|breakage]]. The "Bally Flexometer" named after its inventor is a commonly used instrument and method.. It is also used for [[Car leather|car leather]], [[Leather furniture|furniture leather]], [[Leather clothing|clothing leather]] and other leather applications. |
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | The | + | The change in colour can be checked with measuring devices. The scale of difference is measured in delta value. Delta DEcmc is a number that represents the distance between colours. The deviation results from the variation in the brightness and the shift in the hue. For example, a leather can turn from blue into green, without noticeable changing in the measured brightness. A variation tolerance of delta value of 1 is usually considered acceptable. However, the automotive industry requires a maximum Delta of 0.5, which is difficult to achieve. Surface irregularities of the [[Leather grain pattern - Leather grain texture|grain texture]] or different [[Gloss of Leather|degrees of gloss]] can also change the Delta value. Even within an area, the delta value can vary up to 0.5 due to differences in the grain texture . |
| Line 245: | Line 245: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''The Xenon-tester shows the [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|light sensitivity]]. The [[Finish|finish]] is | + | ''The Xenon-tester shows the [[Colour fastness - Light fastness of leather|light sensitivity]]. The [[Finish|finish]] is recognisable |
faded. DEcmc 6.6.''<br></p> | faded. DEcmc 6.6.''<br></p> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 17 August 2016
Contents
Leather quality
Leather is a natural product and therefore not always equal in quality. There are big differences from one species to another. However, significant differences in skin quality exist from breed to breed even within the same species. In addition, differences also occur due to the gender of the animals, their age, nutrition, feeding and general animal keeping practices. Variations also occur even between animals of same race, same gender, same age, same nutrition and the same animal keeping the skins are not exactly the same, and even within a skin of one animal which therefore lead to differences in leather quality.
Differences in quality of cow leather (but also applies to other species):
- Age: The quality of hides from older animals is generally worse than that of younger animals.
- Gender: Females have a more dense fibre structure and a finer grain structure.
- Gender specific activities: The more often a male animal was used for impregnation and the more often a female animal gave birth, the worse is the stability of the fibre structure of the skin. Castrated oxen tend to have finer skin structure..
- Nutrition: Fresh forage promotes better quality skin.
- Animal keeping: If an animal is kept on open pastures, the texture of the skin is better.
- Climate: A harsh and cold climate favours a good skin quality.
Leather is used for many different applications. As car leather, for shoes, for leather straps and belts, for leather suits or buttery soft leather gloves. Diverse demands are placed on leather, depending on its use. Furniture leather should be easy to maintain, but should also be soft and warm. Shoe leather should be waterproofed, soft, retain heat and robust, yet also remain breathable . A car leather should be easy to maintain and should be impervious to heat, cold and wear.
In all applications, it should not tear, it should be easy to clean, it should not bleach, it schould not smell unpleasant, it should not contain pollutants and it should be durable. All these parameters are summarized as "leather quality" or "leather properties".
In reality, many parameters of the leather properties are in conflict. Leather can`t be buttery soft, robust and easy to clean and maintain at the same time. Leather can't be paper thin and soft and also tearproof at the same time.
In particular, the sensitivity of especially high quality leather like soft aniline leather of a luxury leather jacket, of exotic leather or of an expensive set of furniture are often misjudged. Especially because the object was so expensive customers expect that it would be very easy to clean and maintain the leather. But the reality is the opposite. Such valuable leather has the sensitivity of silk. With regular use the beauty diminishes rapidly, and incorrect cleaning can even ruin the material.
A good leather feels warm and soft, but is also more sensitive.
Particularly car leather is considered to be robust. Most of the vehicle manufacturers require more than 40 quality criteria that must be fulfilled. Stringent wear tests must be passed. The car leather must be resistant to suntan lotion and bug spray. Many chemicals are not allowed to be used and leather emission is tested. As result, the leather is extremely durable, but no longer soft and warm.
The tanner and the producer of a leather object therefore should establish its own, verifiable quality parameters depending on the desired properties of leather and check regularly. The consideration of these parameters starts with the selection of the animal species and the rawhide. Also during the subsequent processing, the differences in the quality of the individual sections of a skin including the possibility of skin damage when cutting must be considered. Additionally in sensitive leathers differences occur from batch to batch. Only a limited quantity of skins can be worked upon at any given time during the manufacturing process of leather and all of them do not behave the same in each run. Often the tanner must intervene in the process by making small changes, which can lead to deviations from batch to batch. Depending on the bandwidth of the established quality limits, differences may be detected.
Apart from the production quality, the longevity of leather depends on certain other factors too. An important element for long lasting pleasure of a of a leather object is the handling of it. If leather is regularly cleaned and maintained and not excessively overused and if the basic rules in dealing with leather are respected, you will prolong the enjoyment of this durable and robust material.
Leather testing - leather properties
To evaluate leather properties there are many different parameters and test methods. For a layman, there are only rough testing options when you want to buy a good and beautiful leather. Some of the criteria can be checked directly as an end customer, but when certain criteria cannot be tested , it always helps to direct the correct questions towards the vendor.
- Look of the leather: A beautiful leather looks very natural and has a defect-free surface.
- Leather grain texture: The grain texture should be good looking and should be as natural as possible. An embossed grain pattern is very uniform, which does not correspond to the natural grain of a skin and embossed leather often feels less natural.
- Softness of the leather: Generally, leather should be pleasantly soft and have a natural feel. But leather shoes or leather belts require a certain strength.
- Haptic evaluation of leather surfaces: A firm leather, as well as all other leather should feel good. This does not include only the softness. A leather can also be expected to feel blunt or smooth. The more beautiful leather feels, the better is the quality of the leather.
- The leather finish: To protect the leather, it is often useful to apply a binder based finish on the leather surface. The more layers of leather paint are applied to leather, the more unnatural it feels. If the grain texture sanded before the finish, the leather feels even more unnatural. Also a film coated leather is less natural, and usually considered to be of inferior quality in comparison to natural leather and therefore relatively inexpensive . But for a patent leather, this effect is an accepted feature.
- Breathability of leather: An advantage of leather over alternative materials is its breathability. But the more a leather is coated with leather colour or a film, the lower is the breathability.
- Tear strength and stability of the leather: Good leather is stable and resistant to tearing, whereby suede and nubuck or extremely soft lambskin can not have the same stability as a belt leather. But within the types of leather there are very different qualities and an inferior quality leather within the same type of leather will always tear more easily in comparison to the higher quality ones. Also sanded leather is usually less stable than full-grain leather.
Criteria of quality leather
To determine whether a leather corresponds to the desired quality requirements, it passes through a series of testing processes. In particular in the automotive industry extremely hight and stict standards are set. But also for furniture, shoe and garment leather minimum qualities are set. In addition, there are statutory testing regulations for harmful substances, which are also a sign of quality.
In the manufacturing of leather the leather quality is constantly checked with all senses and with test equipment.
Although the specific test standards vary by manufacturer and are chosen according to the intended use of the leather, the tested properties are quite uniform.
Further rules on permitted ingredients in leather are regulated by national laws.
Test criteria for the leather quality include (and is regulated in many national and international standards):
- Breathability: The ability to absorb sweat and to submit it to the opposite side.
- Weight: Important e.g. for aircraft leather, because it should weigh as less as possible to reduce fuel costs.
- Thickness of leather: The thickness has an influence on the stability of leather.
- Tensile strenght - Tear strength: If the leather is drawn (for example, more than 200 N per 5 cm).
- Tear force: Leather should not easily tear further (for example, desirable: more than 20 N).
- Adhesiveness of the finish: The colour layers on the surface should not come off (for example, desirable: more than 25 N per 5 cm).
- Flammability and fire retardancy of leather: Important for aircraft, nursing homes, public buildings etc ..
Flame-retardant leather.
- Rub fastness: Dry, wet, alkaline. The surface should not change in friction or wear zones.
- Light fastness: Leather should not fade.
- Flexibility: Desirable: robustness in more than 100,000 cycles. Leather should be extensible, but not baggy.
- Buckling behavior: Leather should not break in folds. Desirable: 30,000 folds without damage.
- Water permeability: Leather should be waterproof.
- Acid and alkali resistance: The leather surface should be resistant to as much as possible chemicals.
- Hydrolysis resistance: Leather should not decay caused by humidity.
- Haptic: Leather should feel accordingly as desired.
- Climate Alternating Test: Leather should be weather-resistant.
- Degree of gloss: Leather should have the desired degree of gloss.
- Back polishing: Leather should not lose the desired gloss level in use.
- Soiling behavior: Leather should not easily get dirty.
- Creaking noise: Leather should not make undesired friction noise when moved.
- Smell: Leather should not smell or it should smell acceptable.
- Leather emission: Leather should not evaporate any substances.
- Alcohol resistance: Drop Test. Resistance to e.g. disinfectants.
- Sea water resistance: Resistance of boat leather to sea water.
Usually material destructive tests are necessary to check the leather quality. - Samples are punched out of the leather.
Due to these stressful testing standards car leather result very similar. Most are monochrome, surface-coloured smooth leather.
Standards of quality leather
There are countless national and international standards to determine the quality of leather. Also, the labelling of leather products is regulated by national and international standards. Additionally many leather manufacturing and processing companies have extra internal standards and requirements.
Overall, the standards set for the quality of leather are correct and necessary. But they are also filled with a lot of grey areas, loopholes and weaknesses.
In Europe, confusing rules exist on labelling of split leather. In some cases it is required to declare and designate the type of leather and in some cases it is not. In Germany for instance, it may happen that coated split leather is used in vehicles, without the obligation to inform the customer. An end user cannot differentiate between the two, When the surface of split leather is embossed with a grain structure it is virtually impossible to tell the difference. In such cases, the standards must do more to ensure transparency, so the customer knows exactly the type of leather they are getting.
Standards are not laws, and judges do not have to follow standards. But in legal disputes standards are often referred and used to find a verifiable solution. However, the inconsistency in different standards causes a lot of confusion. It also does not mention when one particular rule or standard should take priority over the other. An end consumer must be able to find out the quality of the material and be able to compare prices and qualities. The leather standards and norms must do more to protect the end consumer by ensuring dealers, manufacturers provide clear transparent information.
Test equipment
To test the various requirements for leather, there are a wide variety of test devices.
- VESLIC rubbing test: The rubbing test checks the dry abrasion and wet abrasion qualities of leather. Wool felts are rubbed dry and wet in a specified number of times over the leather. The wear in daily use and the prone to discolouration is examined.
VESLIC rubbing test.
- Leather flexometer test: This test examines resistance of the leather to wrinkles. Folding the leather multiple times in all directions allows it to test its resitance.
In particular, shoe upper leather gets buckled during walking and needs a special resistance to breakage. The "Bally Flexometer" named after its inventor is a commonly used instrument and method.. It is also used for car leather, furniture leather, clothing leather and other leather applications.
- Taber abrasion tester: The Taber abrasion tester checks resistance of various materials. The Taber Abraser test is an internationally recognized test method. The Abrasion resistance is generated by two friction rollers that are pressed with a predetermined force to the test material which circularly rotates below the friction rollers. Thereby, a combination of scraping, sliding, squeezing, thwarting and abrasion is simulated.
Taber abrasion tester
- Martindale method: The Martindale rub test examining the abrasion resistance of upholstery leather.
Martindale rub test - Martindale method
The ball plate test simulates selective frictional stress.
- Light fastness - Xenon tester: The xenon tester validates the effect of light on surfaces. Sunlight causes rapid aging of materials. In the test, a xenon arc lamp is used as a radiation source, wherein the filtered spectrum has similarity to the sunlight. The xenon test is suitable for all paints, textiles, plastics etc.
Light fastness test - Aniline leather and semi-aniline are natural and soft, but fade more easily.
The change in colour can be checked with measuring devices. The scale of difference is measured in delta value. Delta DEcmc is a number that represents the distance between colours. The deviation results from the variation in the brightness and the shift in the hue. For example, a leather can turn from blue into green, without noticeable changing in the measured brightness. A variation tolerance of delta value of 1 is usually considered acceptable. However, the automotive industry requires a maximum Delta of 0.5, which is difficult to achieve. Surface irregularities of the grain texture or different degrees of gloss can also change the Delta value. Even within an area, the delta value can vary up to 0.5 due to differences in the grain texture .
At the following photos the xenon test showed a deviation in Delta DEcmc of 6.6 because of fading.
The Xenon-tester shows the light sensitivity. The finish is recognisable
faded. DEcmc 6.6.
Aniline leather day 0, day 16 and day 50 - faded in daily sunlight.
Quality differences
For the end consumer it is difficult to judge the quality of leather. But also experts cannot recognize every quality defect. Experience is needed to discover differences in quality an many quality criteria can only be tested in the laboratory.
All information contained in this dictionary help to understand Leather. For buying furniture, we have an extra instruction.
Basically, price and quality go hand in hand. If a leather object is particularly inexpensive, in most cases it's not valuable. Brand products usually have tested quality.
Grundsätzlich gehen Preis und Qualität Hand in Hand. Ist ein Lederobjekt besonders preiswert, dann ist es i.d.R. auch nicht wertvoll. Markenprodukte sind oft von geprüfter Qualität. Manufacturers who evidently endeavor to improve the quality of their products and to describe the origin and quality of the leather, usually have good qualities. This also applies to the established dealers.
Leather in vehicles have quite rugged qualities due to the purchasing power and strict quality control of the vehicle manufacturer. The leather is not particularly soft and natural, but durable.
Autoleder haben aufgrund derEinkaufsmacht und strengen Qualitätskontrollen der Fahrzeughersteller recht robuste Qualitäten. Das Leder ist zwar nicht besonders weich und warm, aber strapazierfähig. Furniture leathers have greater variation in quality due to the large number of vendors.
Even if the leather is of good substance, with the time the top colouration rubs off caused by wear. The leather itself remains undamaged. Is the leather itself unstable, the leather breaks under the colouration and the colour binder cannot compensate the lack of quality in the fiber composite.
Typical wear in car and furniture leather with good quality.
Typical breakage in leather with poorer quality leather.
Variations in quality
Leather is a natural product. Even within a hide varies the quality of leather, depending on the section of the hide. Therefore it may happen that different leather qualities appear within a leather object. This is often seen in furniture and clothing.
Furniture leather where adjacent areas have different qualities and therefore aged differently.
Furniture leather with different fading behaviour.
This car headrest depending on expression within a small area raises very different wrinkles. In the border region loose grain leather gets visible.
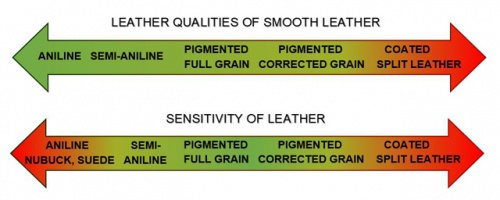
Lederqualitäten der Lederarten und deren Pflegeleichtigkeit
Meist wird davon ausgegangen, dass die beste Lederqualität auch die unempfindlichste und pflegeleichteste sein müsste. Aber wie bei Textilien oder Edelmetallen (Seide ist sehr empfindlich und Gold nicht kratzfest) ist die Empfindlichkeit im höchsten Preis- und Qualitätssegment eher höher. Wertvollere Lederarten müssen oft vorsichtiger und besser gepflegt werden als Preiswertere.
''Comparison of leather quality and ease of maintenance.
Suede - Nubuck - Aniline leather - Semi-aniline - Corrected grain - Coated split leather
Remarks:
- Why is Aniline leather, nubuck and suede less easy to maintain? They are open-pore leather and therefore more sensitive to stains.
- Why is Aniline leather evaluated with best quality? Because aniline leather is especially natural and warm.
- Why is coated split leather less easy to maintain? It is more unstable, what can not be improved by care and classic leather care products harms some types of split leather coatings.
- Are there exceptions to the rules?
LEATHER QUALITY: An aniline leather could theoretically unexpectedly tear or have an undue smell or the leather colour might rub off. Then it is of poor quality. A smooth leather can be fine sanded and carefully embossed and feel like a semi-aniline leather. Then it may be better than a normal, pigmented smooth leather.
But in most cases, the leather corresponds to the expectations. Aniline leather is more expensive because hides without skin damages are rare. Therefore, more effort is applied in the manufacture of such leather.
EASY-CARE: Do the leather fulfill the usual qualities of these types of leather, the given information is accurate. But if a leather is of poor quality, there may occure problems when doing the process of cleaning and maintenance. But this is seldom.
Conclusion: Semianiline leather and pigmented smooth leather are the golden mean for leathers in constant use. They are comfortable, natural and easier to maintain as the remaining types of leather, but also cost a bit more. In the price-sensitive area corrected leather is a good choice.
Additional information
- Typical age-appropriate leather damages and atypical due to quality problems occurring leather damage
- Chrome VI - Chromium VI
- Basic rules when dealing with leather

















































 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution