Difference between revisions of "The biodegradability of leather"
| (2 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Is leather biodegradable?== |
| − | All leather is biodegradable over the long term, but depending on the [[tanning leather|tanning method]] and [[leather production|manufacturing process]], this can happen faster or slower. Before tanning, the animal [[rawhide]] degrades and decomposes very quickly. Skins become [[leather]] through tanning in the [[tannery]] and the tanning process prevents the process of decomposition and makes leather durable and resistant. Durability is one of the main [[leather quality|quality features]] of leather. As leather ages, it becomes more [[Leather damages#Disintegration of old leather|brittle and breaks up]] into small pieces. | + | All leather is biodegradable over the long term, but depending on the [[tanning leather|tanning method]] and [[leather production|manufacturing process]], this can happen faster or slower. Leather is rich in carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, which bacteria and fungi love to eat. |
| + | |||
| + | Before tanning, the animal [[rawhide]] degrades and decomposes very quickly. Skins become [[leather]] through tanning in the [[tannery]] and the tanning process prevents the process of decomposition and makes leather durable and resistant. Durability is one of the main [[leather quality|quality features]] of leather. As leather ages, it becomes more [[Leather damages#Disintegration of old leather|brittle and breaks up]] into small pieces. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''As leather ages, it becomes [[Leather damages#Disintegration of old leather|brittle or cracks]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | + | Under dry conditions, these pieces do not dissolve. Moisture is an important factor in the deterioration of leather. Therefore, [[Leather book cover|books in libraries]] last a long time, but leather exposed to the elements does not last as long in these conditions. | |
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
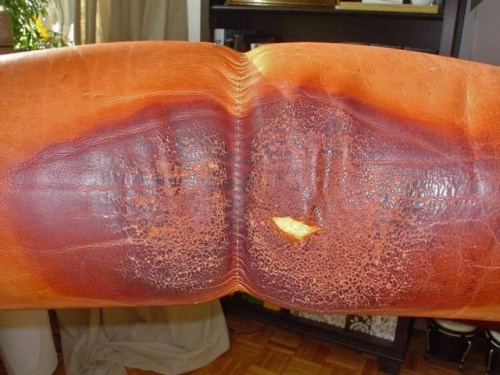
| − | '' | + | ''Leather decay in the [[Leather damages#Grease and sweat stains on leather|contact area with the hair]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | + | However, leather is also [[finish|pigmented]] or [[Coated leather - Laminated leather|coated]]. These substances are mostly polymer-based and some of them are biodegradable, but some, like some types of plastic, do not biodegrade after more than 100 years. Therefore, each [[Types of leather|type of leather]] can and must be tested for biodegradability, and in this way, biodegradability can also be promoted by choosing [[leather production|manufacturing processes]] and chemicals that promote this aspect. In some statistics comparing leather to synthetic matrials, leather is considered to biodegrade in under 50 years and synthetic alternatives take up to 500 years to biodegrade. | |
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Antique [[leather saddle]] from a two-wheeler with signs of decay.''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Additional information == | == Additional information == | ||
Latest revision as of 13:47, 13 June 2023
Is leather biodegradable?
All leather is biodegradable over the long term, but depending on the tanning method and manufacturing process, this can happen faster or slower. Leather is rich in carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, which bacteria and fungi love to eat.
Before tanning, the animal rawhide degrades and decomposes very quickly. Skins become leather through tanning in the tannery and the tanning process prevents the process of decomposition and makes leather durable and resistant. Durability is one of the main quality features of leather. As leather ages, it becomes more brittle and breaks up into small pieces.
As leather ages, it becomes brittle or cracks.
Under dry conditions, these pieces do not dissolve. Moisture is an important factor in the deterioration of leather. Therefore, books in libraries last a long time, but leather exposed to the elements does not last as long in these conditions.
Leather decay in the contact area with the hair.
However, leather is also pigmented or coated. These substances are mostly polymer-based and some of them are biodegradable, but some, like some types of plastic, do not biodegrade after more than 100 years. Therefore, each type of leather can and must be tested for biodegradability, and in this way, biodegradability can also be promoted by choosing manufacturing processes and chemicals that promote this aspect. In some statistics comparing leather to synthetic matrials, leather is considered to biodegrade in under 50 years and synthetic alternatives take up to 500 years to biodegrade.
Antique leather saddle from a two-wheeler with signs of decay.
Additional information
- Leather sustainability and traceability
- Environmental protection
- The Blue Angel
- Oeko-Tex Leather Standard
- Sustainable Leather Foundation SLF
- NATURLEDER IVN certified
- Seal of approval for leather
- Leather quality
- Leather waste













 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution