Difference between revisions of "Frog leather - Toad leather"
m (→Frog leather and toad leather) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Frog leather and toad leather== | ==Frog leather and toad leather== | ||
| − | Frog and toad | + | Frog and toad leathers are quite rare and used mainly for [[Leather handbags|bags]] or other [[Leather accessories|small objects]]. They have a [[Leather grain - Grain side|wart-like surface]], which is partly smoothed in production. |
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Bullfrog== | ==Bullfrog== | ||
| − | + | Ox frogs, also known as giant green frogs or bullfrogs, are predominantly found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. They can be found in countries such as Mexico, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Peru. These frogs inhabit a variety of habitats including rainforests, swamps, ponds, rivers, and even human settlements near water sources. | |
| + | In some regions, particularly in Latin America, ox frogs are consumed as food. Their muscular hind legs, which have a significant amount of meat, are considered a delicacy. Ox frogs are hunted or bred in certain areas to meet the demand for this source of meat. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Eating bullfrog.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''Bullfrog is also eaten.''<br></p> | ||
| + | <p> </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The skin of ox frogs has a unique characteristic. It is [[Leather quality|thick and robust]]. This makes it suitable for [[leather production]]. In countries where ox frogs are found, their skin is used for the production of [[leather]]. The leather is often utilized in the manufacturing of [[Leather wallets|wallets]] and other [[Leather accessories|accessories]]. However, it is important to note that the trade of ox frog leather may be [[CITES - Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of wild fauna and flora|restricted or banned]] in some countries to ensure the conservation of biodiversity and the preservation of natural habitats. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-03.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-02-Ledermuseum-Offenbach.jpg|500px]] | |
| − | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-02-Ledermuseum-Offenbach.jpg| | + | |
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 44: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| + | [[Leather handbags]] from the skin of the bull frog are rarities - especially, when the [[Taxidermy - Hunting trophies - Mounted animals#Animal heads|head is incorporated]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-01.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-0002.jpg|500px]] | |
| − | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-0002.jpg| | + | |
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 58: | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-03-Ledermuseum-Offenbach.jpg| | + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-03-Ledermuseum-Offenbach.jpg|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''[[Leather handbags|Leather handbag]] made of bullfrog leather and bullfrog | + | [[bild:Ochsenfrosch-01-Ledermuseum-Offenbach.jpg|500px]] |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''[[Leather handbags|Leather handbag]] made of bullfrog leather and bullfrog skin seen in the [[Leather museum|DLM - German Leather Museum in Offenbach]].''<br></p> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
==Cane toad== | ==Cane toad== | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-01.jpg| | + | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-01.jpg|500px]] |
</p> | </p> | ||
| − | Cane toads | + | Cane toads were introduced to the Pacific region more than 60 years ago from their natural habitat (South and Central America). The plan was that the toads would provide natural pest control throughout all plantations, from sugar cane to rice. Unfortunately, the experiment proved to be catastrophic for the local fauna. A single adult female can lay more than 30,000 eggs under favourable conditions. The animals can reach a body length of more than 20 cm and a weight of over one kilo. |
| − | Due to the lack of natural enemies and diseases, the | + | Due to the lack of natural enemies and diseases, the cane toad population has increased significantly. They have a voracious appetite, eating nearly everything, including most insects, small animals (lizards, snakes and other amphibians) or little birds. Toads, which occupy huge amounts of natural or artificial waters (especially vestibules), can make the water totally uninhabitable for other animals. |
| − | Since they have | + | Since they have now developed into large pests, they have been officially fought as a plague for many years. The negative ecological consequences caused by their artificial settlement now serve as an example of the enormous risks of uncontrolled and unsupervised biological pest control. |
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-02.jpg| | + | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-02.jpg|500px]] |
| − | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-03.jpg| | + | </p> |
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-03.jpg|500px]] | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| Line 67: | Line 90: | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-04.jpg| | + | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-04.jpg|500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''Cane toad leather objects | + | [[bild:Aga-Kroete-05.jpg|500px]] |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''Cane toad leather objects.''<br></p> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
==Different frog and toad leather types== | ==Different frog and toad leather types== | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | [[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-02.jpg | | + | [[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-02.jpg |500px]] |
| − | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| + | [[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-03.jpg |250px]] | ||
[[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-04.jpg |250px]] | [[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-04.jpg |250px]] | ||
| − | |||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''[[Leather watch strap]] of different frog and toad leather species | + | [[bild:Uhrenarmband-Frosch-Kroetenleder-052.jpg|500px]] |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p align=center> | ||
| + | ''[[Leather watch strap]] of different frog and toad leather species.''<br></p> | ||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== [[Leather videos|Video]] about [[Exotic leather|leather of different animal species]]== | == [[Leather videos|Video]] about [[Exotic leather|leather of different animal species]]== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | <flashow> | + | <flashow>//www.youtube.com/v/-tJtZmJCWLw&fs=1&color1=0x660000&color2=0x550000&border=1|width=500|height=281,25</flashow> |
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:10, 12 June 2023
Contents
Frog leather and toad leather
Frog and toad leathers are quite rare and used mainly for bags or other small objects. They have a wart-like surface, which is partly smoothed in production.
Typical, wart-like surface of the cane toad.
Bullfrog
Ox frogs, also known as giant green frogs or bullfrogs, are predominantly found in tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. They can be found in countries such as Mexico, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Peru. These frogs inhabit a variety of habitats including rainforests, swamps, ponds, rivers, and even human settlements near water sources.
In some regions, particularly in Latin America, ox frogs are consumed as food. Their muscular hind legs, which have a significant amount of meat, are considered a delicacy. Ox frogs are hunted or bred in certain areas to meet the demand for this source of meat.
Bullfrog is also eaten.
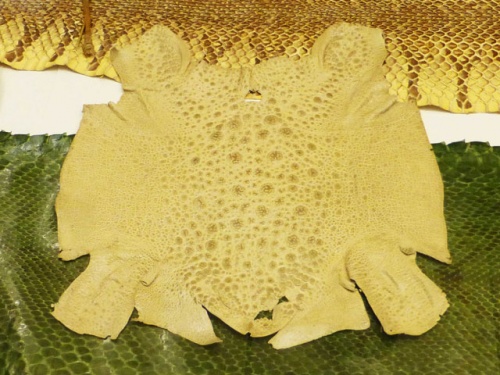
The skin of ox frogs has a unique characteristic. It is thick and robust. This makes it suitable for leather production. In countries where ox frogs are found, their skin is used for the production of leather. The leather is often utilized in the manufacturing of wallets and other accessories. However, it is important to note that the trade of ox frog leather may be restricted or banned in some countries to ensure the conservation of biodiversity and the preservation of natural habitats.
Skin of the bullfrog.
Leather handbags from the skin of the bull frog are rarities - especially, when the head is incorporated.
Leather handbag made of bullfrog leather from about 1930. Head of the bullfrog with glass eyes.
Leather handbag made of bullfrog leather and bullfrog skin seen in the DLM - German Leather Museum in Offenbach.
Cane toad
Cane toads were introduced to the Pacific region more than 60 years ago from their natural habitat (South and Central America). The plan was that the toads would provide natural pest control throughout all plantations, from sugar cane to rice. Unfortunately, the experiment proved to be catastrophic for the local fauna. A single adult female can lay more than 30,000 eggs under favourable conditions. The animals can reach a body length of more than 20 cm and a weight of over one kilo.
Due to the lack of natural enemies and diseases, the cane toad population has increased significantly. They have a voracious appetite, eating nearly everything, including most insects, small animals (lizards, snakes and other amphibians) or little birds. Toads, which occupy huge amounts of natural or artificial waters (especially vestibules), can make the water totally uninhabitable for other animals.
Since they have now developed into large pests, they have been officially fought as a plague for many years. The negative ecological consequences caused by their artificial settlement now serve as an example of the enormous risks of uncontrolled and unsupervised biological pest control.
Cane toads are a plague and are therefore also processed to leather.
Cane toad leather objects.
Different frog and toad leather types
Leather watch strap of different frog and toad leather species.
Video about leather of different animal species
Leather of different animal species - Exotic leather
Other exotic leather
- Alligator leather
- Alpaca fur
- Antelope leather
- Armadillo leather
- Bird leather
- Bull testicles
- Caiman leather
- Camel leather
- Carpincho leather
- Cat fur
- Chicken leather
- Crocodile leather
- Dog leather
- Donkey leather
- Elephant leather
- Fish leather: Eel, shark, salmon, moray eel, stingray and many others
- Giraffe leather
- Hippo Leather
- Horsehide - Horse leather
- Kangaroo leather
- Llama Fur
- Lizard leather
- Ostrich leather
- Pangolin leather
- Peccary leather
- Rumen leather
- Sealskin leather
- Snakeskin
- Turtle skin
- Walrus leather
- Yak leather
- Zebra hide

























 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution