Difference between revisions of "Embossed leather"
| Line 283: | Line 283: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''From behind stabilized emobssing of | + | ''From behind stabilized emobssing of [[leather jacket|leather jackets]].'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 305: | Line 305: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''Very exotic: [[Cow leather]] with an extremely strong embossing and [[Metallic leather| | + | ''Very exotic: [[Cow leather]] with an extremely strong embossing and [[Metallic leather|metallic efect]].'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 314: | Line 314: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Unusually strong [[Formed leather|deformation]] of [[furniture leather]].'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 323: | Line 323: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Embossed [[suede]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| Line 330: | Line 330: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | ''[[ | + | ''[[Crocodile leather|Crocodile]] embossing in [[Imitation leather]].''<br></p> |
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
== Reasons for embossing leather: Correction of the [[Leather grain texture|leather grain pattern]] == | == Reasons for embossing leather: Correction of the [[Leather grain texture|leather grain pattern]] == | ||
| − | + | Another reason for the embossing of leather hides is to hide skin [[natural markings on leather]]. Therefore the surface is [[Sanding leather|sanded]], repaiered and embossed. Such leather is called ‘corrected grain’. | |
| − | + | A farmer doesn’t get any more money from the butcher for his cows and cattle, if the skin is flawless. Often the animals in their lifetime suffer [[natural markings on leather|wounds and diseases]] that affect the quality of the leather surface. To hide insect bites, injuries, illnesses and other damages on animal skins, cattle hides are commonly given an uniform grain embossing. | |
| − | + | This reduces the [[Leather cutting waste|waste]] of the leather, as the entire surface of a skin gets an uniform [[Leather grain - Grain side|grain pattern]]. All parts of a set of [[furniture leather|furniture]] or [[car leather|car interiors]] will be identical. Minor flaws and irregularities of the natural grain can be balanced and must not be circumvented when [[Leather cutting|cutting]] the leather. | |
=== [[Leather grain texture]] === | === [[Leather grain texture]] === | ||
| − | + | A natural [[Leather hair pores - Hair follicles#fine pore leather - coarse pore leather - fine grain leather - coarse grain leather|leather grain]] is different across the skin surface. In the middle of a skin the leather is mostly fine grained, and toward the edge it is coarse grain. | |
| + | |||
| + | When [[Leather cutting|cutting]] seating surfaces for [[leather furniture|furniture]] and [[car leather|vehicles]], the customers value a uniform grain structure. Due to the uniform embossing, the grain structure is identically all over the hide. | ||
| Line 351: | Line 353: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''On one hide: [[Leather hair pores - Hair follicles#fine pore leather - coarse pore leather - fine grain leather - coarse grain leather|fine grain]] - transition - [[Leather hair pores - Hair follicles#fine pore leather - coarse pore leather - fine grain leather - coarse grain leather|coarse grain]].'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
=== Unembossed leather === | === Unembossed leather === | ||
| − | + | The number of skins which can be processed rises and lowers costs. Skins that are not good enough for processing as [[Full grain leather|full-grain leather]] can be embossed. Only about 10-20% of the hides coming from the slaughterhouse are ‘good’ to ‘very good’ [[leather quality|quality]]. Embossing is no loss of quality, as long as no damage is hidden under the embossing that affects the life expectency of the leather. | |
| Line 365: | Line 367: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Unembossed leather. - The hair pores are still visible (click to enlarge).'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
===Corrected Grain - sanded and embossed leather === | ===Corrected Grain - sanded and embossed leather === | ||
| − | + | As preparation for embossing, the leather is mostly [[Sanding leather|surface-sanded]] to obtain an uniform structure. Such leather is called ‘Corrected Grain’. Such leather is cheaper and is more [[Haptic evaluation of leather surfaces|plastic-like and colder]].Also the [[Breathability of leather|breathability]] is significantly lower than with [[Leather hair pores - Hair follicles|porous leathers]]. There is also leather which is only lightly [[Sanding leather|sanded]] and nicely [[Haptic evaluation of leather surfaces|soft and warm]]. But this is more the exception. | |
| Line 379: | Line 381: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p align=center> | <p align=center> | ||
| − | '' | + | ''Embossed and [[Sanding leather|sanded]] leather. - The [[Leather hair pores - Hair follicles|hair follicles]] are sanded away and over embossed.'' |
</p> | </p> | ||
=== Embossed leather without [[Sanding leather|sanding]] === | === Embossed leather without [[Sanding leather|sanding]] === | ||
| − | + | To prevent too poor hides [[Sanding leather|being sanded]] and embossed, sanding is in some cases forbidden by the car manufactured. This avoids beein cheated. | |
Revision as of 18:07, 3 December 2016
Contents
The embossing of leather
Embossing refers to the modification of the natural grain of an animal skin by pressing or rolling a new scar design. Embossments can cover the entire surface of a skin but there is also the possibility to characterise local individual motifs. Embossing is caused by pressing, rolling or stamping.
Types of embossing
- Blind Embossing, blind printing, blind finishing: Embossing of leather without colour.
- Gold embossing: The transfer of gold leaf into the embossing.
- Colour imprint: The transmission of colour by colour films in the embossment.
Different embossing on book covers: BBlind Embossing - Gold embossing - Colour imprint.
The parameters that influence the embossing:
- The pressure with which the tools are pressed into the leather -> The higher the pressure, the stronger and more durable the Embossing.
- The time required for the stamping -> The longer the stamping pressure, the stronger and more durable the Embossing.
- The temperature at which is marked -> The hotter the tool, the stronger and more durable the Embossing.
- The moisture of the leather -> Imprints in damp leather is clearer and more durable.
The leather to be embossed sometimes is previously bonded with foam and lining on the backside so the embossed pattern sits neatly and stays permanently deepened. Sometimes a fabric is glued to the backside to prevent stretching and flattening of the embossed motif. Particularly deep motifs need to be stabilised by filling in the depth of the embossing. There is wide variety of filling materials that can be used. From paper mache to hot glue, the decisive factor is the stability and flexibility of the filler material.
Embossing after pigment colouration. The fold was not embossed.
The embossing roller of an embossing machine in a leather factory.
Embossing plates: coarse grain leather and pig skin grain.
Crocodile pattern by embossing plate.
Embossing stamps are milled. VOLVO-Logo embossed in car leather (www.ledermanufaktur.com). - Embossing in a Porsche.
Embossing in the imitation leather of a Ford Mustang.
Due to the longer exposure time at a hydraulic press, the embossed motif is more stabel than with an embossing roller. Depending on the temperature, pressure and dwell time, the embossing is more or less clear and stabel. Moituring the leather addtionally stabelizes the motifs.
The fine tuning determines the result. Too hot embossed aircraft leather does not fit to "First Class".
Embossing rollers and embossing stamps are expensive. Individual motifs are therefore often carved. There is also the possibility to bring motifs on leather by lasers.
Embossed furniture leather.
Embossed lamb leather used for clothing.
Beautiful embossing on a strap made of elkskin leather (Pineyard - MUD GbR).
Almost any type of leather can be embossed. However, the embossing must be adjusted according to the type of leather. The resistance of an embossing depends on the embossing process. The higher the pressure and the temperature, and the more moisture in the leather, the more permanent the reshaping of the fibre. But of course there are also limits to the pressure and temperature that can be applied to each leather.
Reasons for embossing leather: To provide leather with designs
Often, leather is decorated in order to achieve a certain look. Also the grain structure of other animals is copied. Even for experts is somtiemes difficult to distinguish if the grain structure is original from the animal or only an embossed copy.
A video about painting on leather, perforating leather, carving leather, embossing leather and several other methods to create motifs on leather.

|
165px | 
|
| Embossed leather belt. | Embossed seat cushion. | Embossed antique weapon shield. |
| 165px | 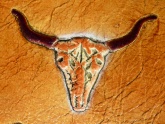
|

|
| Embossed case. | Embossed and decorated with paint. | Embossed skin structure of ostrich leather. |

|
165px | 
|
| Embossed antique leather. | Beautiful motif. | Very finely worked. |

|
165px | 
|
Antique leather folder from 1920 with beautiful embossing.
Leather handbags producers like to brand by embossing their company logos.
Antique leather chairs are often decorated with beautiful motif.
Modern patterns embossed in cow leather.
Front and back side horse motive embossing.
Horse stamping tool positive and negative as pictures above. - Two other variants of horse motifs as embossing tool.
Usually embossing is done on the top compressing the leather grain structure. The uncompressed leather fibres remain above. This creates the three-dimensionality. Leather is sometimes embossed with two embossing plates from both sides (positive and negative). Then the recesses on the back must be stabilized to not press done the emobossed motif in use.
In case of strong embossments in soft leathers, these are stabilized from the back by a silicone filling to avoid that the embossing can not be pressed pressed down from the front.
From behind stabilized emobssing of leather jackets.
Antique Leather with a waxy reinforcement (wax mixed with sand) at the back side.
Very exotic: Cow leather with an extremely strong embossing and metallic efect.
Unusually strong deformation of furniture leather.
Embossed suede.
Crocodile embossing in Imitation leather.
Reasons for embossing leather: Correction of the leather grain pattern
Another reason for the embossing of leather hides is to hide skin natural markings on leather. Therefore the surface is sanded, repaiered and embossed. Such leather is called ‘corrected grain’.
A farmer doesn’t get any more money from the butcher for his cows and cattle, if the skin is flawless. Often the animals in their lifetime suffer wounds and diseases that affect the quality of the leather surface. To hide insect bites, injuries, illnesses and other damages on animal skins, cattle hides are commonly given an uniform grain embossing.
This reduces the waste of the leather, as the entire surface of a skin gets an uniform grain pattern. All parts of a set of furniture or car interiors will be identical. Minor flaws and irregularities of the natural grain can be balanced and must not be circumvented when cutting the leather.
Leather grain texture
A natural leather grain is different across the skin surface. In the middle of a skin the leather is mostly fine grained, and toward the edge it is coarse grain.
When cutting seating surfaces for furniture and vehicles, the customers value a uniform grain structure. Due to the uniform embossing, the grain structure is identically all over the hide.
On one hide: fine grain - transition - coarse grain.
Unembossed leather
The number of skins which can be processed rises and lowers costs. Skins that are not good enough for processing as full-grain leather can be embossed. Only about 10-20% of the hides coming from the slaughterhouse are ‘good’ to ‘very good’ quality. Embossing is no loss of quality, as long as no damage is hidden under the embossing that affects the life expectency of the leather.
Unembossed leather. - The hair pores are still visible (click to enlarge).
Corrected Grain - sanded and embossed leather
As preparation for embossing, the leather is mostly surface-sanded to obtain an uniform structure. Such leather is called ‘Corrected Grain’. Such leather is cheaper and is more plastic-like and colder.Also the breathability is significantly lower than with porous leathers. There is also leather which is only lightly sanded and nicely soft and warm. But this is more the exception.
Embossed and sanded leather. - The hair follicles are sanded away and over embossed.
Embossed leather without sanding
To prevent too poor hides being sanded and embossed, sanding is in some cases forbidden by the car manufactured. This avoids beein cheated.
Embossed, but not sanded leather. The hair pores are still clearly visible.
Car leather from BMW with "Montana" embossment. - Strong embossed furniture leather. - BMW with "Picasso" embossment.
Other possibilities how to provide leather with designs
- Carving leather
- Laser engraving - Laser cutting leather
- Perforated leather
- Hole punching
- Embroidery
- Leather seams
- Leather imprint
- Formed leather
- Painting on leather
- Braided leather
- Leather etching & engraving
- Leather tattoo
- Glued leather strips
- Burning designs on leather
Additional information







































































 a kotori web solution
a kotori web solution